Last week, the U.S. Department of Agriculture reported that a pig at a backyard farm in Oregon had been infected with bird flu.
As the bird flu situation continues to evolve, now we have learned that the A/H5N1 strain of the virus infects a spread of animals, including quite a lot of birds, wildlife and dairy cattle.
Fortunately, now we have not seen sustained spread of the virus between people at this stage. However, the detection of the virus in pigs represents a worrying development in the trajectory of this virus.
How did we get here?
The most concerning sort of bird flu currently circulating is clade 2.3.4.4b A/H5N1, the influenza A strain.
Since 2020, the A/H5N1 2.3.4.4b virus has spread to a big selection of birds, wildlife and livestock which have never previously been infected with avian influenza.
While Europe is a hotspot for A/H5N1, attention is currently focused on the US. In 2024, dairy cattle were infected for the first time, with over The problem affects 400 herds in a minimum of 14 US states.
Bird flu has huge consequences for breeding and industrial food production, as infected poultry flocks should be slaughtered and infected cows may result in contamination dairy products. That said, pasteurization should make the milk secure to drink.
Although farmers have suffered heavy losses as a consequence of H5N1 bird flu, it may well also mutate to cause a pandemic in humans.
Birds and humans have various kinds of receptors in their respiratory tract to which influenza viruses attach, corresponding to a lock (receptors) and a key (virus). The attachment of the virus allows it to enter the cell and body and cause disease. Avian influenza viruses are adapted to birds and spread easily amongst birds but not in humans.
So far, human cases have mainly occurred in individuals who stayed at the facility close contact with infected livestock or birds. In the US, the majority were agricultural employees.
The fear is that the virus will mutate and adapt to humans. One key step for this to occur could be to vary the virus’s affinity from bird receptors to receptors found in the human respiratory tract. In other words, if the virus “key” has mutated to raised fit the human “lock”.
Recent testing of sample A/H5N1 2.3.4.4bz infected person, disturbing results were obtainedidentifying mutations in the virus which will increase transmission between human hosts.
Why are pigs an issue?
A pandemic strain of influenza in humans can arise in several ways. One involves close contact between humans and animals infected with their very own specific influenza viruses, creating opportunities mixing of genes of avian and human viruses.
Pigs are the perfect vessel for mixing genes to supply a human strain of pandemic flu because they’ve receptors in their respiratory tract that each avian and human influenza viruses it may well get tied up.
This signifies that pigs will be infected with each avian influenza virus and human influenza virus. These viruses can exchange genetic material, mutate and simply transmit to humans.
Conversation, CC BY-SA
Interestingly, there have been pigs in the past less vulnerable to A/H5N1 viruses. However, the virus has recently mutated they infect pigs more easily.
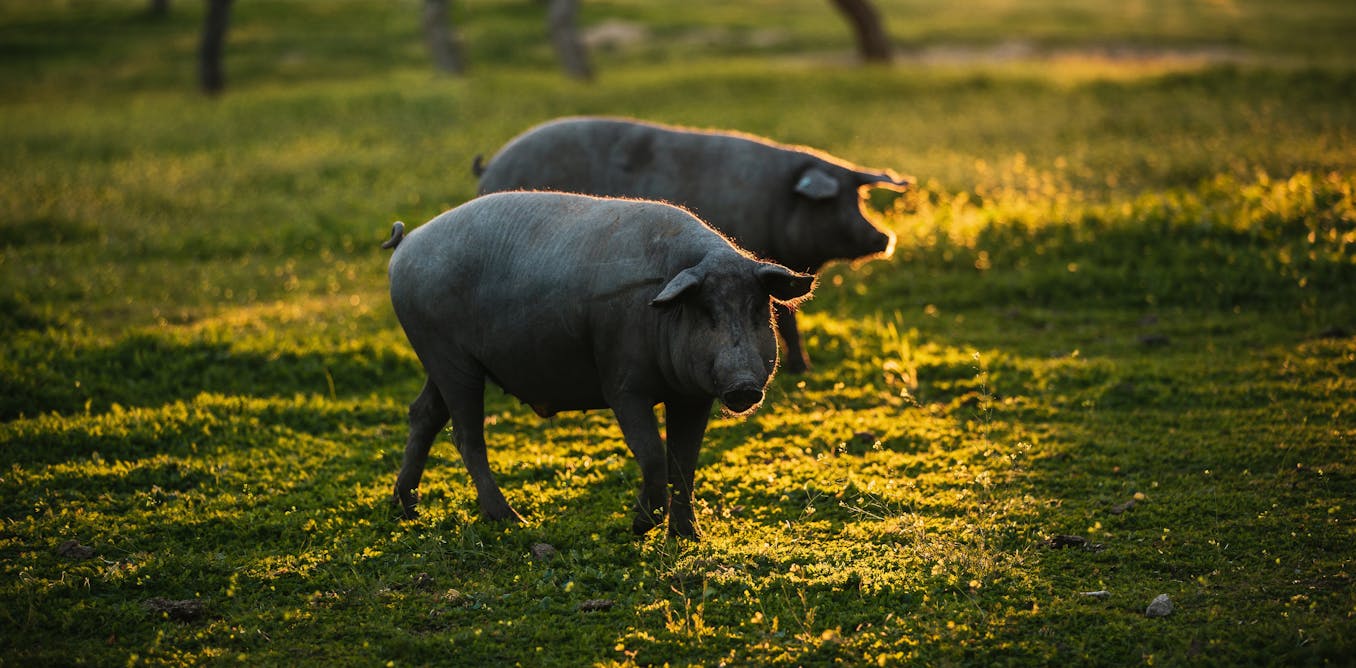
In a recent case in Oregon, A/H5N1 was detected in a pig on a non-commercial farm following an outbreak of disease amongst poultry kept on the same holding. This A/H5N1 strain originated from wild birdsand never the one common in US dairy cows.
Pig infection is a warning. If the virus makes its way into industrial piggeries, it might create a much higher level of pandemic risk, especially as winter approaches in the U.S., when seasonal human flu cases begin to extend.
How can we minimize the risk?
Surveillance is vital to early detection of a possible pandemic. This includes comprehensive testing and reporting of infections in birds and animals financial compensation and support measures for farmers to encourage timely reporting.
Strengthening global surveillance of influenza is crucial because unusual spikes in pneumonia and severe respiratory illnesses could signal a human pandemic. Our EPIWATCH system looks for early warnings of such activity, which can accelerate vaccine development.
If a cluster of human cases occurs and influenza A is detected, further testing (called subtyping) is vital to find out whether it’s a seasonal strain, an avian strain resulting from transmission of the virus, or a brand new pandemic strain.
Early identification can prevent a pandemic. Any delay in identifying an emerging pandemic strain allows the virus to spread widely across international borders.
The first human case of A/H5N1 in Australia was in a baby who became infected while traveling in India and was hospitalized for the disease in March 2024. Tests then identified influenza A (which might have been seasonal influenza or bird flu), but subtype to discover A/H5N1 was delayed.
This sort of delay may very well be costly if human-borne A/H5N1 emerges and is taken into account seasonal influenza because the influenza A test is positive. 5% of positive tests for influenza A undergo further subtyping in Australia and most countries.
In light of the current situation, there needs to be a low threshold for subtyping influenza A strains in humans. Rapid tests that may tell the difference between seasonal flu and H5 A flu are emerging and may form a part of governments’ pandemic preparedness.
The risk is higher than ever before
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that the current risk posed by H5N1 to the general public stays low.
However, with the H5N1 virus already in a position to infect pigs and showing worrying mutations in adapting to humans, the risk level has increased. Given that the virus is so common amongst animals and birds, the statistical probability of a pandemic is higher than ever before.
The excellent news is that we’re higher prepared for a flu pandemic than other pandemics because vaccines will be produced in the same way as seasonal flu vaccines. Once the genome of the pandemic flu virus is understood, vaccines will be updated to match it.
Partially matched vaccines and a few are already available countries corresponding to Finland vaccinate high-risk farm employees.