Lifestyle
10 years after Ferguson, black students are still more likely to be expelled from schools
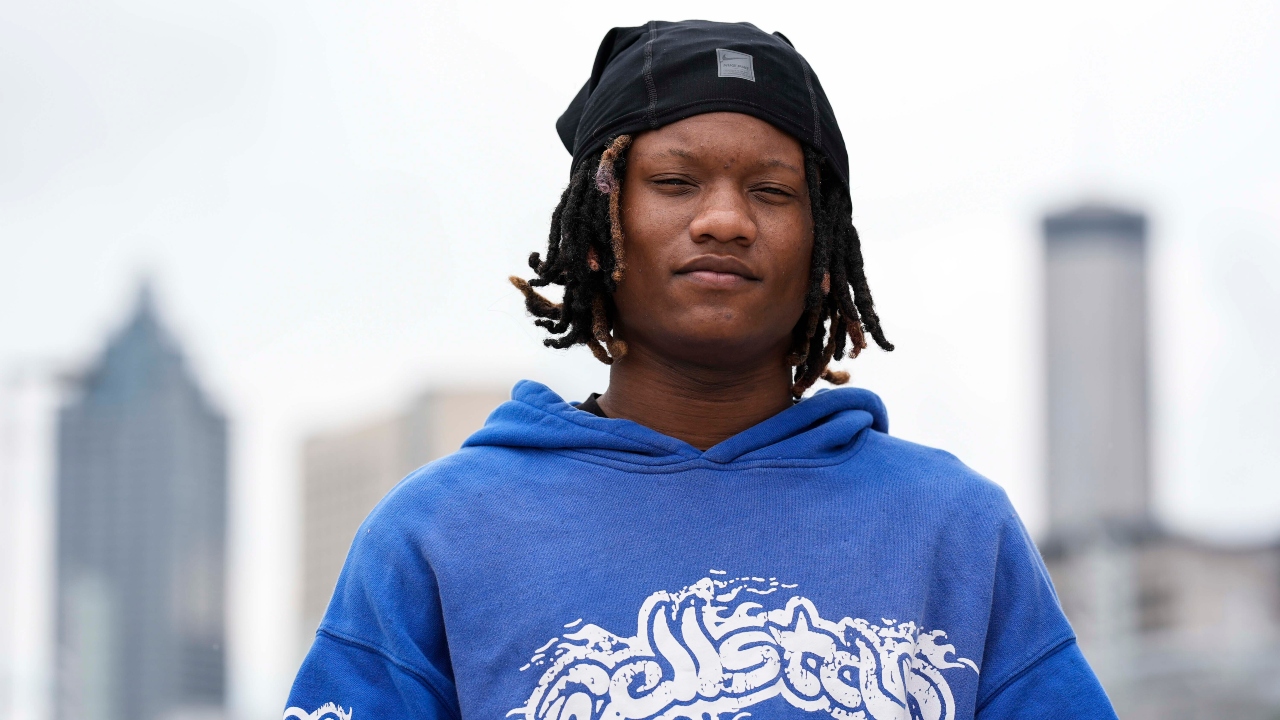

Before he was suspended, Zaire Byrd was thriving. He acted at school plays, played on the football team, and worked out with other athletes. He had never been suspended before—he had never even been arrested.
But when Byrd got right into a fight after school sooner or later, none of that seemed to matter to administrators. Byrd said he was defending himself and two friends when three other students threatened to rob them. Administrators at Tri-Cities High School in Georgia called the fight a “gang fight”—an automatic 10-day suspension. After a disciplinary hearing, they sent him to an alternate school.
This experience almost ruined his education.
“The last four years have been really big for me, from online learning to being suspended,” said Byrd, who began highschool remotely through the pandemic. “I could have learned more, but between all that and changing schools, it was tough.”
In Georgia, black students like Byrd make up just over a 3rd of the population. But they make up nearly all of students who receive punishments that take them out of sophistication, including suspension, expulsion and transfer to an alternate school.
These disparities in Georgia and across the country became the goal of a newly energized reform movement a decade ago, spurred by the identical racial reckoning that gave rise to the Black Lives Matter movement. For many advocates, students and educators, pursuing racial justice meant addressing disparate outcomes for black youth that begin within the classroom, often through harsh discipline and underinvestment in low-income schools.
There has been some progress in lowering suspension rates for black students previously decade. But stark disparities persist, according to a review of discipline data in key states by The Associated Press.
In Missouri, for instance, an AP evaluation found that black students served 46% of all suspension days within the 2013-14 school yr — the yr Michael Brown was shot and killed by police within the state days after his highschool graduation. Nine years later, that percentage dropped to 36%, according to state data obtained through a public records request. Both numbers far exceed the share of black students in the coed population, which is about 15%.
In California, the suspension rate for black students dropped from 13 percent in 2013 to 9 percent a decade later — still thrice the suspension rate for white students.
Gradual progress, but advocates say prejudice stays
The national counting on race has elevated the concept of the “school-to-prison pipeline” — the notion that being kicked out of faculty or dropping out increases the likelihood of being arrested and imprisoned years later. School systems have made incremental progress in reducing suspensions and expulsions, but advocates say underlying biases and structures remain in place.
Consequence: More and more black children are being expelled from schools.
“This obviously fuels the school-to-prison pipeline,” said Terry Landry Jr., Louisiana policy director for the Southern Poverty Law Center. “If you’re not in school, what are you doing?”
Students who are suspended, expelled, or otherwise removed from class are more likely to be suspended again. They change into more distant from their classmates and are more likely to change into disengaged from school. They also lose time learning and are likely to have lower academic outcomes, including grades and graduation rates.
Still, some schools and policymakers have doubled down on exclusionary discipline because the pandemic. In Missouri, students lost nearly 780,000 days of instruction due to in- or out-of-school suspensions in 2023, the best number in a decade.
In Louisiana, black students are twice as likely to be suspended as white students and receive longer suspensions for a similar infractions, according to a 2017 study by the Education Research Alliance for New Orleans. But a brand new law takes effect this yr that recommends expelling any highschool or middle school student who’s suspended thrice in a single school yr.
Teachers and fogeys try to ensure children attend school
Federal guidelines for addressing racial disparities at school discipline were first issued by President Barack Obama’s administration in 2014. Federal officials urged schools not to suspend, expel or refer students to law enforcement except as a final resort, and encouraged restorative justice practices that didn’t force students out of the classroom. Those policies were rolled back by President Donald Trump’s administration, but federal and state civil rights laws still mandate the gathering of discipline data.
In Minnesota, the expulsion and suspension rate for black students dropped from 40% in 2018 to 32% 4 years later — still nearly thrice higher than the speed of black students in the general population.
The disciplinary gap within the state was so glaring that in 2017, the Minnesota Department of Human Rights ordered dozens of districts and charter schools to enter into legal settlements over disciplinary practices, particularly for Black and Native American students. In those districts, the department found, nearly 80% of disciplinary consequences issued for subjective reasons reminiscent of “disruptive behavior” were for students of color. School buildings were closed for many of the fiscal yr due to the pandemic, so it’s hard to tell whether schools have made progress since then.
Featured Stories
Khulia Pringle, an education advocate in St. Paul, said her daughter was repeatedly suspended. The harsh discipline led her down a improper path. At one point, Pringle said, her daughter wanted to drop out of faculty.
Pringle, then a history and social studies teacher herself, left her job to change into a baby advocate, hoping to offer one-on-one support to families experiencing harsh school discipline.
“That’s when I really started to notice that it wasn’t just me. Every black parent I worked with called me about suspensions,” she said.
Education reform quickly emerged as a goal of the Black Lives Matter movement. In 2016, when the Vision for Black Lives platform was finalized, it included a call for an education system that recognized students’ cultural identities, supported their mental and physical health, and didn’t subject them to unreasonable searches, seizures, and arrests in schools.
“We need to end mass incarceration and mass criminalization, and that starts in schools,” said Monifa Bandele, a political leader with the Movement for Black Lives. “The data shows that with every expulsion or suspension, students are more likely to end up in the criminal justice system.”
As Linda Morris, an attorney on the American Civil Liberties Union, said, black students are not only punished more harshly, but in addition they receive harsher punishments than their white peers for similar and even the identical behavior.
“Students of color are often not given the same opportunities as their white peers and can even be perceived as having harmful motives,” Morris said.
Attention to these disparities has led to some changes. Many districts have adopted restorative justice practices that aim to address the basis causes of behavior and interpersonal conflicts moderately than simply suspending students. Schools have increased their investment in mental health resources.
And for a time, some districts, including Chicago and Minneapolis, had been working to remove police from schools. Those efforts gained recent momentum in 2020 after the killing of George Floyd in Minnesota by a white police officer.
Schools take tougher approach to discipline after pandemic
Calls for tougher discipline and more police involvement have resurfaced in recent years as schools struggled to cope with misbehavior after months of closure due to the pandemic.
Activists point to a deeper reason for the discipline efforts.
“This response is also, in some ways, a response to the progress that’s been made,” said Katherine Dunn, director of the Opportunity to Learn program on the nonprofit Advancement Project. “It’s a response to organizing. It’s a response to the power that black, brown and other young people have built in their schools.”
After his suspension, Byrd, a Georgia student, was sent to an alternate discipline program. A district spokesman said this system is designed to help students proceed their education and receive social and emotional support during discipline.
Byrd said he waited in line every day to be searched from head to toe before being allowed to enter the constructing, a process the district says is a preventive measure and is run by the corporate that runs the choice school.
“It definitely changed him,” said his mother, DeAndrea Byrd. “He wasn’t excited about school. He wanted to quit. It was incredibly difficult.”
Byrd finished his third yr at an alternate school. He transferred to one other public school for his senior yr, where he felt supported by the administration and was able to graduate. He has since found a job close to home and plans to attend an HBCU in Alabama, where he hopes to study cybersecurity.
As Byrd reflects on the fight and its aftermath, he said he wishes the varsity had treated him like a child who had never been in trouble before, as an alternative of kicking him out.
(*10*) he said. “None of us should be punished for one mistake.”
Lifestyle
Gocha Hawkins gives the taste of brunch in the new cookbook

Gocha Hawkins still impresses with a gourmet in Atlanta and beyond because of its new cookbook focused on classic favorite brunch.
Gocha Hawkins has already gained a brand on the Food Atlanta stage. Former hairdresser It became An experienced restaurateur with two hotspots, Tapas and Gocha breakfast bar, in her name. Now he offers its own recipes in the new cookbook to recreate its characteristic dishes in your personal kitchen.
The cookbook accommodates 90 recipes that could make every morning, from spicy shrimps and gritts to vegan, but fragrant, cauliflower steak. Hawkins, a self -proclaimed “pancake connoisseur”, knows his path after every kitchen, proven by her at all times full restaurants that captivated the Atlantians.
Hawkins began after moving to the southwestern side of Atlanta in 2014. She noticed how limited food options were in this area, and decided to take the opportunity to bend her own chef’s skills. Hawkins talked Black company About how this transition helped her use her passions, while raising this underestimated community.
“In 2014, I moved to the south -western part of the city and I was like WOW, this community is in an adverse situation,” she shared To be Director of IDA Harris digital content.
“There is nothing here except the restaurant chain. I thought (I thought) that it would be an ideal opportunity to open a breakfast restaurant, because it was missing in my area.”
According to Hawkins, this plant led to the Empire of food outside its wildest dreams. After starting the first restaurant in 2018, her ability to adapt to the needs of her clients, comparable to the opening of a truck with food during a pandemic, led her to a continuing and growing success despite the unpredictable food industry.
After leaving the door, she expanded her cascading location of the breakfast bar to double its capability, taking on the neighboring space that closed the activity. While the surrounding firms got here and left, Hawkins became a choice to take care of its flagship location in the heart of its area.
“I think this is something that many black districts will affect, but you decided to stick to. I feel that investing in the community is extremely important,” Hawkins explained.
“It is that the most important thing is that the brand invests in the community, you know how to ensure work and simply developing our community at all. I have the impression that I do not return the community, in this way we are another restaurant of the great network, you know? I feel that small companies have so many opportunities to use community stimulation.”
What makes Hawkins dishes so unique is that there was no clear recipe behind them. Although she has chosen the direction of food since then, what led to the innate chef is her personal taste and desire for meals that simply tasted good. However, he still emphasizes the importance of nutrition in the development of the menu.
“The way I eat and the way I cook at home is what I wanted to bring to the restaurant, because I knew that it would be suitable for everyone. (Everyone) I want to be much healthier now, they go to this direction and want to create recipes that are easy, aromatic and comfortable.”
Employing over a 12 months and a half, to place their recipes, fans of southern browchy could make cooking comfortable. He also offers insight into its retail line, allowing readers to recreate their hot sauce and pancakes to assume a breakfast bar at home again.
Hawkins doesn’t wish to add anything to a community that doesn’t serve it, whether on its menu or a business portfolio. From gifts to eating to coats, Hawkins pours back to those that eat together with her.
The entrepreneur also wants her employees to prosper, offering subsidies for workers attending studies. As for what he plans to serve, Gocha will expand to the joint kitchen to assist chefs who cannot afford a brick space. The introduction at the Atlantic station under the GOCHA restaurant brand brand, the possibility of helping other emerging chefs in getting the leg stays part of Hawkin’s vision.
“The advice for every entrepreneur would be to study everything you are trying to do and gain knowledge,” she concluded.
“Invest in yourself and you will undoubtedly get some noses. So when you get these no, don’t give up. Continue investing in yourself and just continue.”
Pre -sale orders are Available now.
(Tagstranslaner) Atlanta Restaurants
Lifestyle
6 to take out from the New York Times article on a decrease in record levels for black men, especially in HBCUS

On March 30, New York Times abandoned the story entitled “In Black COlleges, a stubborn difference in sex records is still growing, “which discusses quite commonly understood occurrence of historically black universities and universities (HBCUS): there are various more black women who don’t attend black women.
In this particular profile, Howard University is the center of the universe of the article, and the song opens quite fascinating statistics: “Howard, one of the most elite historically black universities and universities in the country, there are only 25% of people – 19% black men.” The remainder of the article is deep in what this may mean for the entire black community (not only Howard, but the lack of black men in college), black women, especially in terms of economic burdens and marriage prospects, and the way this statistics looks in real time for students in Howard. There is a lot to go out of the article that’s price discussing, but I’ll focus on several thoughts that I had after reading.
1
I don’t mean that this article is useless or a waste of time – our stories require more telling; He screams to the reporter Clyde McGrady – but I talked about every thing about every thing discussed in this article with my classmates in Morehouse College and Spelman College in the late Nineteen Nineties and with my students at the Howard University in the Nineteen Twenties. Apparently, the difference in saving sex increases, which seems crazy since it seemed huge once I was a student. Shoot, for lots of us men who went to HBCus, the actual sales point was that there are three women for each man no matter HBCU. And I’m not even close to jokes.
2. Saying this, as an adult, I have a look at these items with a much greater perspective and care.
When I used to be a student, I didn’t really take into consideration the long -term implications of this huge gap between the variety of black men with black women enrolled in studies. I believed that it implies that I should find a partner. As an adult, I saw this gap influenced the lives of many black women that I do know. I do know a significant variety of black women who’re late 30 and 40 years old, with a very small variety of marriage perspectives. Sure, there are various aspects that may affect the ability of a person to connect with someone, but not having individuals with whom they’re incompatible, that is a problem. When I used to be 23, I believed that each one this might work for all my friends in the marriage/relationship department; At the age of 45, this reality looks rather more tragic. And so, women can marry men who would not have educational achievement, but when we’ve to imagine that educational achievements lead to higher financial perspectives, it may well be safely said that black women who’re still ahead of even white women for lifetime earnings, remain to bear financial burden on the household, that are fair, traditionally, can include their very own problems.
3. Using Howard as a central point is interesting, but it’s also suitable for money.
As a one who taught classes at the Howard University of Limited Sample of 4 semesters, I can check this statistics. Of the 4 classes I had, she did not have a single student. On average, two and up to 4 for classes around 16-18 students. Now, in my class, it didn’t make it difficult or influenced the class in any way, and I’d put up for the most part. But it was immediately noticeable and as I said, I’m now an adult, looking to the future and I see how so few students are to influence the future. I talked to students about how they perceive dates in Howard, and well, as an example that they perceive it similar to in AUC in the Nineteen Nineties – guys have a significant advantage and everybody knows it.
4. I actually have no proof of this, but I bet the creator’s economy had a significant impact on this conversation.
I can not say how often I actually have heard students-I know the way I know the way I do know through my niece and nephews in my student age, tell me that their goal is to “earn money” and “grind”. This is generally the answer to the query of what they intend to do with their directions. A brief answer, they don’t know. Meanwhile, I do know many individuals who’ve placed the creator of the content (more likely that they put the “entrepreneur”) on their tax forms and can implement traditional educational funds, because the money on YouTube is there. I’m not saying that black men determine not to go to studies due to Instagram, but College has already lost a part of their splendor; The ability to earn money from the phone while laying paper and avoiding classes sounds even for me, a black man with many degrees. There is already pressure to earn money to sustain with the legendary Joneses, but should you don’t see the value in college, and it costs $ 50,000 or more, you’ll be able to give it up for fast dollars, which seem to be a celebrity on Instagram, regardless of how short life might be.

5. If you do not see individuals who appear to be you might be doing various things, it’s possible you’ll not realize that you could do it.
I do know that it sounds trashy, but for me this article is in one necessary thing that I believe most of us understand: the representation matters. The article says that the health care industry wants more black people in this field. There are many studies that show the influence of teaching black men. When you not see yourself represented in these spaces, because black men not go along these roads, it significantly changes the landscape of the black community and our aspirations.
6. I don’t know how to solve this problem.
My guess is that nobody else does, because if someone knew how to get the variety of black men in college, they’d do it. However, I do know that the cost of studying doesn’t help in any respect. When I went to Morehouse College, it was about USD 16,000 a 12 months. Now, according to to the websiteMore houses costs around USD 56,000. This implies that 4 -year education will last not less than USD 150,000, assuming that you simply are moving from the campus and also you eat a weight loss program to study over the last three years. This will not be attractive to anyone. However, that is a problem that requires a solution, because, as the article suggests, the black family, black wealth and the black community depend on it.

(Tagstranslate) @Ap
Lifestyle
Three-book Stephen Curry Treok-Book
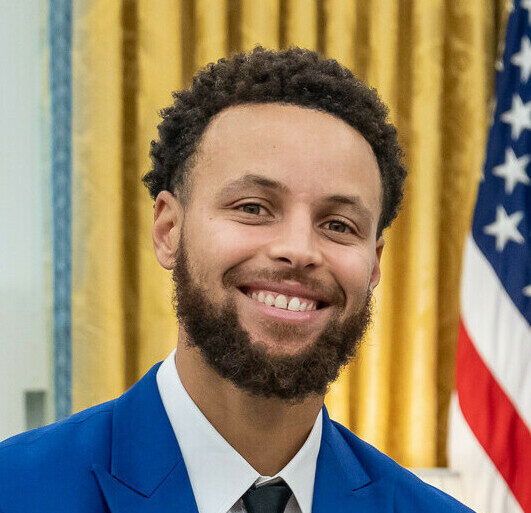

Golden State Warriors Superstar Point Guard Stephen Curry and One World, Random House Publishing Group Imprint, announced on March 29 that curry and print agreed to 3 books, with the primary book “Shot Ready”, which debuted on September 9.
According to the press message of 1 world, Curry Will Draw your personal journey In the hope of inspiring people from the background different from his own to fulfill the challenges of their lives.
“I want to use my history to connect with people from different environments and help them solve the mystery of their own potential,” said Curry in a press release. “This book is a holiday of a work that happens in the shade, creativity that drives every move, and mindfulness that ground me. I hope” Shot Ready “inspires readers to accept their own journey, trust of the process and always find joy in pursuit of perfection.”
According to books, they will even be published in cooperation with Unirimous Media, a multimedia company that’s working on the production of an enchanting family, faith and sports content for a wide selection of centuries that Curry and Erick Peyton began in 2018. The book, which is a tough book within the variety of coffee, is currently available to order first.
“Shot Ready” is a multimedia project that accommodates over 100 photos of curry and its personal reflections. Like curry, publishers settle the book as a distillation of their personal philosophy of success, focused on readers who want to attain full potential. The book is currently on sale for USD 41.85 on the Pnguin Random House bookstore.
“Shot Ready” is a strong distillation of Stephen Curry’s transformation philosophy of success-condemned on preparation, constant improvement, creativity, combination, mindfulness and joy-dressed in his unmatched voice and magnificence. Stunningly designed and illustrated by over 100 great photos, “ready to be shot” is an intimate narrative and a practical plan of the reading room that wishes to boost its own potential. ” One world.
As described by the imprint mission on the Penguin Random House, Curry’s Multimedia Company and One World Publishing website, they appear to adapt the missions.
“The mission of one world is to provide a home for the authors – Nowierów, Eses, memories, poets, journalists, thinkers, activists and creative artists unlimited by the species – who undermine the status quo, burden the dominant narratives and gives us a new language to understand our past, present and future. Our writers represent voices with all spectrum Universal stories about the changing world. ” The publisher stated.
In addition to curry, one world counts Tina Knowles, Anelise Chen, Heather McGhee, Keshia N. Blain, Ibrahim X. Kendi, Ta-Nehisi Coates, Donovan X.
(Tagstotransate) shot readad
-

 Press Release12 months ago
Press Release12 months agoU.S.-Africa Chamber of Commerce Appoints Robert Alexander of 360WiseMedia as Board Director
-

 Press Release1 year ago
Press Release1 year agoCEO of 360WiSE Launches Mentorship Program in Overtown Miami FL
-

 Business and Finance10 months ago
Business and Finance10 months agoThe Importance of Owning Your Distribution Media Platform
-

 Business and Finance1 year ago
Business and Finance1 year ago360Wise Media and McDonald’s NY Tri-State Owner Operators Celebrate Success of “Faces of Black History” Campaign with Over 2 Million Event Visits
-

 Ben Crump12 months ago
Ben Crump12 months agoAnother lawsuit accuses Google of bias against Black minority employees
-

 Theater1 year ago
Theater1 year agoTelling the story of the Apollo Theater
-

 Ben Crump1 year ago
Ben Crump1 year agoHenrietta Lacks’ family members reach an agreement after her cells undergo advanced medical tests
-

 Ben Crump1 year ago
Ben Crump1 year agoThe families of George Floyd and Daunte Wright hold an emotional press conference in Minneapolis
-

 Theater1 year ago
Theater1 year agoApplications open for the 2020-2021 Soul Producing National Black Theater residency – Black Theater Matters
-

 Theater10 months ago
Theater10 months agoCultural icon Apollo Theater sets new goals on the occasion of its 85th anniversary












 (@wardeiicurry30)
(@wardeiicurry30) 






