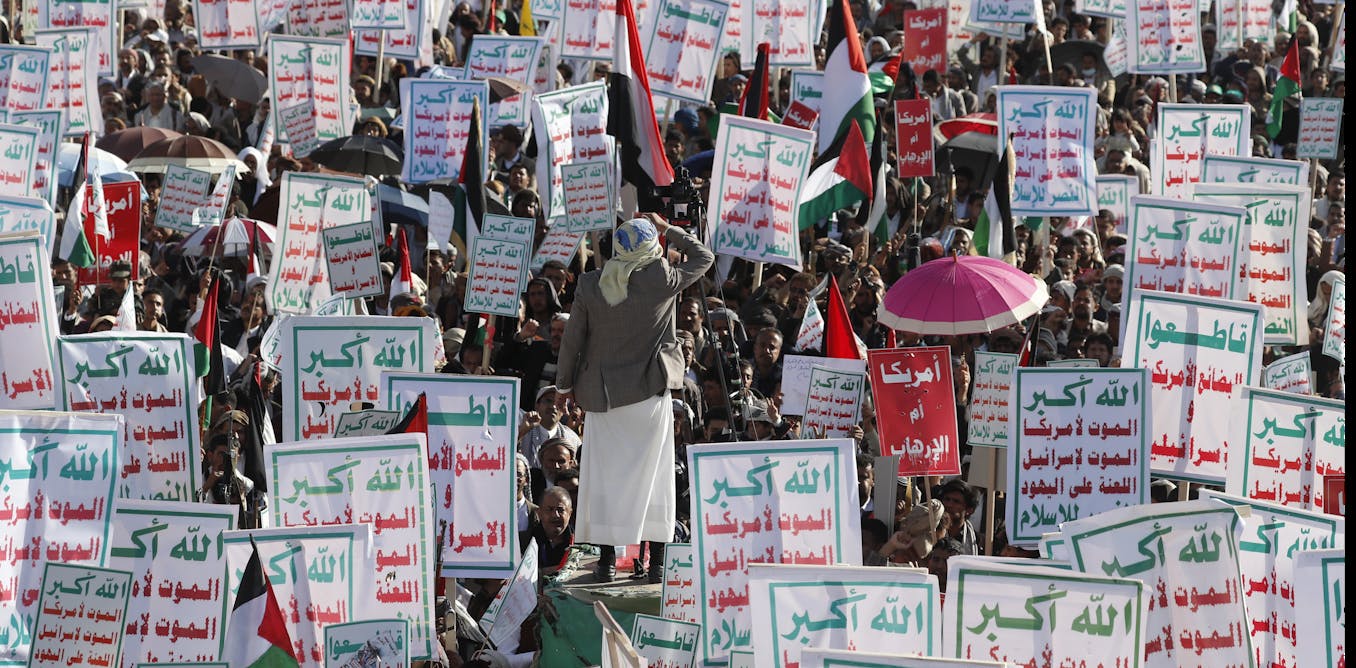
Houthi fighters in Yemen still interfere with shipping in the Red Sea, undeterred by increasing Western air raids or by changing the group’s designation to “global terrorist” organization. As the attacks intensified, the group’s slogan (or , meaning “scream”) also gained notoriety.
Banners line the streets of Houthi-controlled Yemen and are waved by supporters at their rallies. He declares: “God is great, death to America, death to Israel, curse to the Jews, victory to Islam.” (Mentions of Houthi enemies appear in red reminder font barbed wire).
Many commentators are quick to indicate the origins of this phenomenon motto from the Iranian Revolution. The link reveals a long-standing relationship between the Houthis and their foremost regional supporter, Iran.
It also carries an anti-imperialist message, which has attracted some outside analysts overestimate local legitimacy of the Houthis and reduce suffering peculiar Yemenis living under their brutal and exclusionary rule.
Since the Houthis were reclassified as a worldwide terrorist organization, a special slogan has dominated posters at their rallies. On a red background there is the inscription: “America is the mother of terrorism.”
At first glance, it appears to be an extension of the ideological sentiments conveyed in .
But the slogan also reflects the complexity of Yemen’s views on U.S. counterterrorism interventions and the widespread belief that they’ve provided terrorist groups with the oxygen they should survive.
Terrorist groups as a tool of the state
The United States has long been criticized disproportionately killing civilians in anti-terrorist attacks. Some experts say it could actually create more “terrorists” than he kills.
Another criticism: it was originally supported by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). Osama bin Laden and the mujahideen in Afghanistan in an try and trap the Soviet Union in an unwinnable war, holding the United States no less than somewhat responsible for what followed.
However, there are other layers to those slogans which might be less intuitively understood by Western audiences.
The West’s knee-jerk support for authoritarian leaders who claim to focus on terrorism is widely seen in Yemen (and across the Middle East) as fueling symbiotic relationships between oppressive regimes, terrorist groups and Western-led military interventions.
For many individuals in the region, groups like al-Qaeda and Islamic State function partly as “tools” that Western-backed authoritarian leaders use to keep up their power. They provide credible denial of the violence that leaders use against civilians or support their position that “If I’m gone, terrorists will take over the country“.
Militant site / AP / uncredited
In Yemen, there have long been allegations that Western-backed leaders:
Western regional partners similar to Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates are also accused recruitment members of al-Qaeda fight IN paramilitary forces against Yemeni adversaries.
As a result, many Yemenis wouldn’t view al-Qaeda or the Islamic State as completely separate from those that rule the country. Rather, they often view these terrorist groups as helping to bolster the established order.
This view is, of course, diametrically against the Western understanding of Al-Qaeda or the Islamic State. In the West, these groups are portrayed as rebels in search of to overthrow the state. However, across the region, many individuals consider that these relationships defy easy categories similar to “state versus rebel” or “friend versus foe” because terrorist groups might be each.
One Yemeni analyst stated that frustration attempts to elucidate the symbiotic relationship between terrorist groups and authoritarian leaders in the Middle East:
It’s easier to inform a baby that Santa Claus doesn’t exist than to persuade foreigners what Al-Qaeda in Yemen really is.

Yahya Arhab/EPA
Why Western policies are counterproductive
For the Houthis, America’s alleged role in helping fuel terrorist groups has long been part of the group’s message.
More than a decade ago – two years before the Houthis seized Yemen’s capital and sparked a long-running war – I visited a northern town where there have been several large, freshly painted murals that read “Al-Qaeda is American-made“.
When I asked residents about this, they looked as if it would consider the statement a trivial statement of fact. They were more impressed by the “nice handwriting” than the content. (Like the symbol banners, the murals use a red barbed wire font for the word “America.”)
The Houthi’s message about American complicity in terrorism resonates since it operates on several levels.
It points to the violence unleashed by the US-led invasion and occupation of Iraq almost unconditional the support the US provides to Israel, and military, carceral AND political the support of the US and its Western partners ensures authoritarian leaders in the region.

Jim Lo Scalzo/EPA
What is also striking is the deep sense in Yemen (and across the region) that the political established order is being maintained by brutal regimes. And that terrorist groups like al-Qaeda – and the counterterrorism interventions they invite – contribute to those regimes staying in power.
Of course, the violence that the Houthis use to keep up their power is an irony that shouldn’t be forgotten. The Houthis are widely despised by Yemenis living under their rule. Still, their message echoes common views about the causes of regional violence that some Western observers have long rejected.
Indeed, the complexities underlying the new Houthi slogan help explain why Western policies across the region will proceed to backfire.
Simply put, people in the region consider that Western policymakers are blind to their historical achievements in strengthening the enemies they arrive to fight. The incontrovertible fact that Western airstrikes are giving the Houthis a legitimacy that was previously unimaginable is ominous.
Unfortunately for Yemeni civilians, the Houthi’s stance toward Israel will increase their attractiveness to those that know little about what life is like with them. It may also make it even harder for the Yemenis to remove them from power.