Technology
The creators of a short video using Sora technology explain the strengths and limitations of AI-generated videos
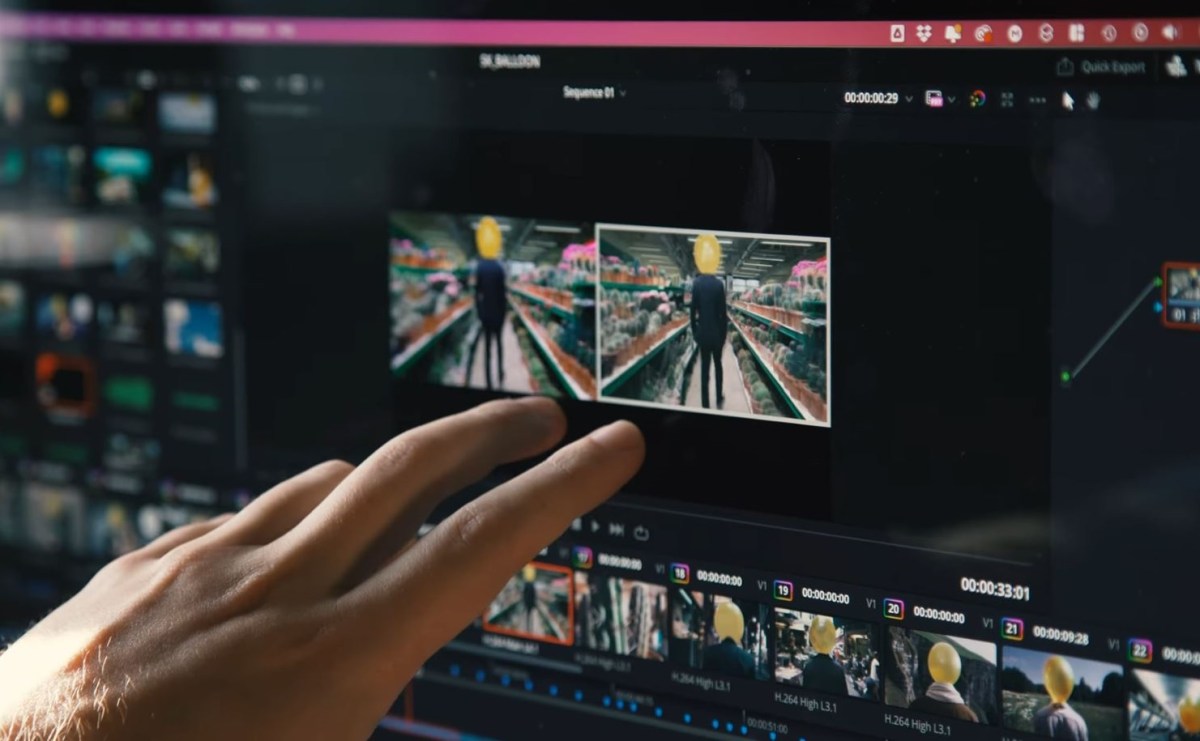
OpenAI’s video generation tool Sora surprised the AI community in February with smooth, realistic video that appears to be well ahead of the competition. However, there are a lot of details unnoticed of the rigorously choreographed debut – details that were filled in by a filmmaker who was given advance access to create a short film starring Sora.
Shy Kids is a Toronto-based digital production team that has been chosen as one of only a few by OpenAI for the production of short movies essentially for OpenAI promotional purposes, although they got considerable creative freedom in creating an “air head”. In fxguide visual effects news interviewpost-production artist Patrick Cederberg described “actually using Sora” as part of his work.
Perhaps the most significant takeaway for many is that this: while OpenAI’s post highlighting the short movies allows the reader to assume that they were created roughly fully shaped by Sora, the reality is that they were skilled productions, equipped with solid storyboarding, editing, color correction, and publish work equivalent to rotoscoping and visual effects. Just like Apple says “recorded on iPhone” but doesn’t show the studio setup, skilled lighting, and color work after the fact, Sora’s post only talks about what it allows people to do, not how they really did it.
The interview with Cederberg is interesting and quite non-technical, so in the event you are in any respect interested, go to fxguide and read. But listed below are some interesting facts about using Sora that tell us that, while impressive, this model is maybe less of a step forward than we thought.
Control is the most desired and most elusive thing at this moment. … The only thing we could achieve was simply hyper-descriptive tooltips. Clarifying the character’s attire, in addition to the type of balloon, was our way of ensuring consistency, since from shot to shot/generation to generation there just isn’t yet a feature arrange to offer full control over consistency.
In other words, things which are easy in traditional filmmaking, equivalent to selecting the color of a character’s clothing, require complex workarounds and controls in the generative system because each shot is created independently of the others. This could change, of course, but it surely’s definitely rather more labor intensive lately.
Sora’s prints also needed to be watched for unwanted elements: Cederberg described how the model routinely generated a face on a balloon that the foremost character has for a head, or a string hanging from the front. They needed to be removed by mail, one other time-consuming process in the event you couldn’t get a prompt to exclude them.
Precise timing and character or camera movements aren’t actually possible: “There is a little bit of temporal control over where these different actions are happening in a given generation, but it’s not precise… it’s kind of a shot in the dark,” Cederberga said.
For example, synchronizing a gesture equivalent to a wave is a very approximate and suggestion-based process, unlike manual animations. And a shot that appears like a panorama pointing upwards at a character’s body may or may not reflect what the filmmaker wanted – so on this case, the team rendered the shot in a vertical orientation and cropped it in post. The generated clips also often played in slow motion for no particular reason.
An example of Sora’s shot and its ending at a glance. Image credits: Shy children
In fact, the use of on a regular basis film language equivalent to “swipe right” and “tracking shot” was generally inconsistent, Cederberg found, which the team found quite surprising.
“Scientists weren’t really thinking like filmmakers before they turned to artists to play with this tool,” he said.
As a result, the team performed a whole lot of generations, each lasting 10–20 seconds, and ended up using only a handful. Cederberg estimated the ratio at 300:1, but of course we might all be surprised at the ratio for a regular photo.
A band, actually he made a little behind-the-scenes video explaining some of the issues they bumped into in the event you’re curious. Like much AI-related content, the comments are quite critical of the whole project — though not as insulting as the AI-powered promoting we have seen pilloried recently.
One last interesting caveat concerns copyright: If you ask Sora to share a Star Wars clip, he’ll refuse. And in the event you attempt to get around this “man in robes with a laser sword on a retrofuturistic spaceship” problem, he may also refuse because by some mechanism he recognizes what you are attempting to do. She also refused to take an “Aronofsky-style shot” or a “Hitchcock zoom.”
On the one hand, it makes total sense. However, this begs the query: If Sora knows what it’s, does that mean the model has been trained on that content to raised recognize that it’s infringing? OpenAI, which holds its training data cards near the vest – to the point of absurdity, as in CTO Mira Murati’s interview with Joanna Stern – he’ll almost definitely never tell us.
When it involves Sora and its use in filmmaking, it’s definitely a powerful and useful gizmo as an alternative, but its purpose just isn’t to “create films from whole footage.” Already. As one other villain famously said, “that will come later.”
Technology
Trump to sign a criminalizing account of porn revenge and clear deep cabinets

President Donald Trump is predicted to sign the act on Take It Down, a bilateral law that introduces more severe punishments for distributing clear images, including deep wardrobes and pornography of revenge.
The Act criminalizes the publication of such photos, regardless of whether or not they are authentic or generated AI. Whoever publishes photos or videos can face penalty, including a advantageous, deprivation of liberty and restitution.
According to the brand new law, media firms and web platforms must remove such materials inside 48 hours of termination of the victim. Platforms must also take steps to remove the duplicate content.
Many states have already banned clear sexual desems and pornography of revenge, but for the primary time federal regulatory authorities will enter to impose restrictions on web firms.
The first lady Melania Trump lobbyed for the law, which was sponsored by the senators Ted Cruz (R-TEXAS) and Amy Klobuchar (d-minn.). Cruz said he inspired him to act after hearing that Snapchat for nearly a 12 months refused to remove a deep displacement of a 14-year-old girl.
Proponents of freedom of speech and a group of digital rights aroused concerns, saying that the law is Too wide And it will probably lead to censorship of legal photos, similar to legal pornography, in addition to government critics.
(Tagstransate) AI
Technology
Microsoft Nadella sata chooses chatbots on the podcasts

While the general director of Microsoft, Satya Nadella, says that he likes podcasts, perhaps he didn’t take heed to them anymore.
That the treat is approaching at the end longer profile Bloomberg NadellaFocusing on the strategy of artificial intelligence Microsoft and its complicated relations with Opeli. To illustrate how much she uses Copilot’s AI assistant in her day by day life, Nadella said that as a substitute of listening to podcasts, she now sends transcription to Copilot, after which talks to Copilot with the content when driving to the office.
In addition, Nadella – who jokingly described her work as a “E -Mail driver” – said that it consists of a minimum of 10 custom agents developed in Copilot Studio to sum up E -Mailes and news, preparing for meetings and performing other tasks in the office.
It seems that AI is already transforming Microsoft in a more significant way, and programmers supposedly the most difficult hit in the company’s last dismissals, shortly after Nadella stated that the 30% of the company’s code was written by AI.
(Tagstotransate) microsoft
Technology
The planned Openai data center in Abu Dhabi would be greater than Monaco

Opeli is able to help in developing a surprising campus of the 5-gigawatt data center in Abu Dhabi, positioning the corporate because the fundamental tenant of anchor in what can grow to be considered one of the biggest AI infrastructure projects in the world, in accordance with the brand new Bloomberg report.
Apparently, the thing would include a tremendous 10 square miles and consumed power balancing five nuclear reactors, overshadowing the prevailing AI infrastructure announced by OpenAI or its competitors. (Opeli has not yet asked TechCrunch’s request for comment, but in order to be larger than Monaco in retrospect.)
The ZAA project, developed in cooperation with the G42-Konglomerate with headquarters in Abu Zabi- is an element of the ambitious Stargate OpenAI project, Joint Venture announced in January, where in January could see mass data centers around the globe supplied with the event of AI.
While the primary Stargate campus in the United States – already in Abilene in Texas – is to realize 1.2 gigawatts, this counterpart from the Middle East will be more than 4 times.
The project appears among the many wider AI between the USA and Zea, which were a few years old, and annoyed some legislators.
OpenAI reports from ZAA come from 2023 Partnership With G42, the pursuit of AI adoption in the Middle East. During the conversation earlier in Abu Dhabi, the final director of Opeli, Altman himself, praised Zea, saying: “He spoke about artificial intelligence Because it was cool before. “
As in the case of a big a part of the AI world, these relationships are … complicated. Established in 2018, G42 is chaired by Szejk Tahnoon Bin Zayed Al Nahyan, the national security advisor of ZAA and the younger brother of this country. His embrace by OpenAI raised concerns at the top of 2023 amongst American officials who were afraid that G42 could enable the Chinese government access advanced American technology.
These fears focused on “G42”Active relationships“With Blalisted entities, including Huawei and Beijing Genomics Institute, in addition to those related to people related to Chinese intelligence efforts.
After pressure from American legislators, CEO G42 told Bloomberg At the start of 2024, the corporate modified its strategy, saying: “All our Chinese investments that were previously collected. For this reason, of course, we no longer need any physical presence in China.”
Shortly afterwards, Microsoft – the fundamental shareholder of Opeli together with his own wider interests in the region – announced an investment of $ 1.5 billion in G42, and its president Brad Smith joined the board of G42.
(Tagstransate) Abu dhabi
-

 Press Release1 year ago
Press Release1 year agoU.S.-Africa Chamber of Commerce Appoints Robert Alexander of 360WiseMedia as Board Director
-

 Press Release1 year ago
Press Release1 year agoCEO of 360WiSE Launches Mentorship Program in Overtown Miami FL
-

 Business and Finance12 months ago
Business and Finance12 months agoThe Importance of Owning Your Distribution Media Platform
-

 Business and Finance1 year ago
Business and Finance1 year ago360Wise Media and McDonald’s NY Tri-State Owner Operators Celebrate Success of “Faces of Black History” Campaign with Over 2 Million Event Visits
-

 Ben Crump1 year ago
Ben Crump1 year agoAnother lawsuit accuses Google of bias against Black minority employees
-

 Theater1 year ago
Theater1 year agoTelling the story of the Apollo Theater
-

 Ben Crump1 year ago
Ben Crump1 year agoHenrietta Lacks’ family members reach an agreement after her cells undergo advanced medical tests
-

 Ben Crump1 year ago
Ben Crump1 year agoThe families of George Floyd and Daunte Wright hold an emotional press conference in Minneapolis
-

 Theater1 year ago
Theater1 year agoApplications open for the 2020-2021 Soul Producing National Black Theater residency – Black Theater Matters
-

 Theater12 months ago
Theater12 months agoCultural icon Apollo Theater sets new goals on the occasion of its 85th anniversary