Technology
Atomos Space’s first orbital mission is a trial by fire
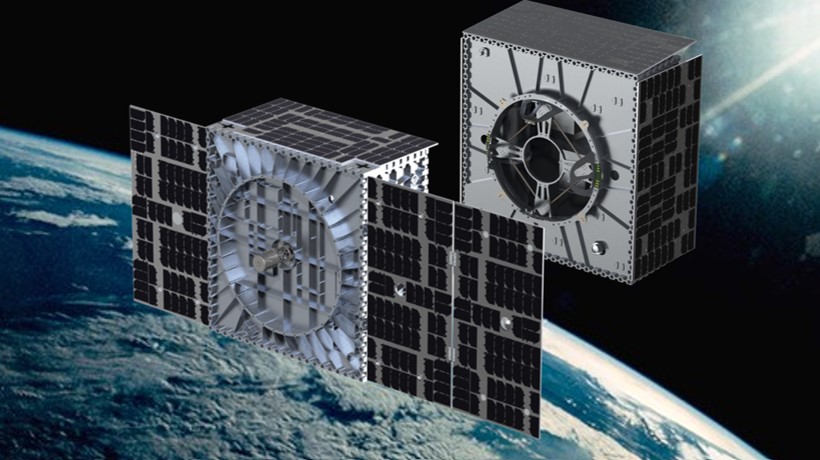
Few missions more vividly embody the maxim “space is hard” than Atomos Space’s first demonstration mission, which the corporate managed to drag back from the brink of disaster – greater than once.
This demonstration mission, called Mission-1, was launched into orbit on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket on March 4. The mission’s goals are extremely ambitious: the 2 spacecraft – an orbital transfer vehicle called Quark-LITE and a goal vehicle called Gluon – will ultimately reveal extremely complex maneuvers, including rendezvous, docking, orbital transfer and in-orbit refueling.
The company faced two major problems related to communication and the rotation rate of the spacecraft – and (largely) solved each problems despite massive limitations, sparse data packets, and very limited bandwidth. (So limited, in reality, that the team needed to limit flight software updates to a text string of just 145 characters).
“It was relentless,” Atomos CEO and co-founder Vanessa Clark told TechCrunch.
William Kowalski, COO and co-founder of the corporate, agreed. “What makes it so difficult is that even in our situation, we’re trying to extrapolate the status of a very complicated system from maybe 100 bytes of data,” he said. “That’s a lot. You guess what’s causing it, knowing that a few of those guesses could lead on you down a path from which you may never get well.”
Problems began just hours after the 2 interconnected spacecraft were launched from the Falcon 9 upper stage. The deployment was nominal, and Atomos received the first signal from the spacecraft seven minutes after deployment. The mood was solemn.
But 40 minutes passed before the corporate received one other signal. Then eight hours.
Atomos expected data packets every jiffy.
“The worst (day) was Monday, when we took off, that evening,” Kowalski said. “It was 11 p.m. at night, it was me and the chief engineer… and we didn’t hear anything and we just think: Have we failed? Did they die? We gave it a shot, but it just didn’t work. It was really a punch in the gut.”
Mission controllers didn’t discover the basis cause until 24 to 48 hours after deployment, and did so with the assistance of one other company with on-orbit assets. After pulling some strings, they managed to speak on the phone to the chief systems engineer of the satellite communications company Iridium. The spacecraft used third-party modems that used the Iridium intersatellite link network and likewise used the Iridium constellation as relay satellites. The Atomos spacecraft was moving too fast and in direct contrast, it couldn’t perform a data “handshake” with the Iridium satellites to truly transmit the knowledge back to Earth.
Atomos engineers implemented a series of software updates that reduced duty cycles and ensured that the radios would all the time be on, even when the spacecraft was in a low-power state.
When engineers tried to resolve the communication problem, nevertheless, they encountered one other problem: the spacecraft was rolling at an especially high rate of 55 degrees per second (they were designed to deal with roll rates of as much as 5 degrees per second). In addition, the spacecraft slowly rotated in order that the solar panels not faced the sun. This meant it was a race against time and the spacecraft’s batteries completely depleted.
“We had two charts,” Kowalski said. “We plotted our power trend for when we predict we will probably be facing away from the sun and have (at) zero power, in addition to the sink rate. The removal rate needed to be delivered to zero before the ability dropped to zero.
The problem was exacerbated by limited communication; teams weren’t in a position to definitively confirm that anything was mistaken until the fourth day after deployment, and the spacecraft could only process recent commands between long periods of what were essentially communications blackouts.
Slowly, over the course of several days, they managed to slow the spacecraft down. The team achieved one other major victory after they were able to ascertain high-bandwidth communications, a space-to-space link on a Quark-LITE device communicating via the Inmarsat network. On Thursday, the corporate made its first attempt at establishing broadband connectivity and successfully maintained communication with the spacecraft for six minutes.
During this era, mission controllers received 17 times more data than since launch. As a result, mission controllers received enormous amounts of information on the state of the spacecraft. The news wasn’t all positive – certainly one of the OTV batteries was badly damaged by aggressive cycling and it appears the GPS aboard certainly one of the spacecraft needed to be reset – but these are easy fixes, Clark said.
The company plans to begin commissioning the drive system on Tuesday or Wednesday. If all goes in response to plan and engineers determine that the support system provides accuracy and aiming control, they are going to test operation without torque bars and response wheels. The company intends to deploy the spacecraft inside about a month, with all mission objectives expected to be achieved by the top of June.
Kowalski and Clark attribute a part of the startup’s success to the incontrovertible fact that it is highly vertically integrated. The team, which worked 100 hours per week within the first week after deployment, was in a position to use their in-depth knowledge of spacecraft design to resolve emerging problems.
“It was obviously very painful, but it is reminiscent of the words of the CEO of Nvidia: ‘I wish you great suffering.’ We went through it and it wasn’t great at the moment, but now that we’ve gotten there, we’re definitely better,” Clark said.
Technology
Trump to sign a criminalizing account of porn revenge and clear deep cabinets

President Donald Trump is predicted to sign the act on Take It Down, a bilateral law that introduces more severe punishments for distributing clear images, including deep wardrobes and pornography of revenge.
The Act criminalizes the publication of such photos, regardless of whether or not they are authentic or generated AI. Whoever publishes photos or videos can face penalty, including a advantageous, deprivation of liberty and restitution.
According to the brand new law, media firms and web platforms must remove such materials inside 48 hours of termination of the victim. Platforms must also take steps to remove the duplicate content.
Many states have already banned clear sexual desems and pornography of revenge, but for the primary time federal regulatory authorities will enter to impose restrictions on web firms.
The first lady Melania Trump lobbyed for the law, which was sponsored by the senators Ted Cruz (R-TEXAS) and Amy Klobuchar (d-minn.). Cruz said he inspired him to act after hearing that Snapchat for nearly a 12 months refused to remove a deep displacement of a 14-year-old girl.
Proponents of freedom of speech and a group of digital rights aroused concerns, saying that the law is Too wide And it will probably lead to censorship of legal photos, similar to legal pornography, in addition to government critics.
(Tagstransate) AI
Technology
Microsoft Nadella sata chooses chatbots on the podcasts

While the general director of Microsoft, Satya Nadella, says that he likes podcasts, perhaps he didn’t take heed to them anymore.
That the treat is approaching at the end longer profile Bloomberg NadellaFocusing on the strategy of artificial intelligence Microsoft and its complicated relations with Opeli. To illustrate how much she uses Copilot’s AI assistant in her day by day life, Nadella said that as a substitute of listening to podcasts, she now sends transcription to Copilot, after which talks to Copilot with the content when driving to the office.
In addition, Nadella – who jokingly described her work as a “E -Mail driver” – said that it consists of a minimum of 10 custom agents developed in Copilot Studio to sum up E -Mailes and news, preparing for meetings and performing other tasks in the office.
It seems that AI is already transforming Microsoft in a more significant way, and programmers supposedly the most difficult hit in the company’s last dismissals, shortly after Nadella stated that the 30% of the company’s code was written by AI.
(Tagstotransate) microsoft
Technology
The planned Openai data center in Abu Dhabi would be greater than Monaco

Opeli is able to help in developing a surprising campus of the 5-gigawatt data center in Abu Dhabi, positioning the corporate because the fundamental tenant of anchor in what can grow to be considered one of the biggest AI infrastructure projects in the world, in accordance with the brand new Bloomberg report.
Apparently, the thing would include a tremendous 10 square miles and consumed power balancing five nuclear reactors, overshadowing the prevailing AI infrastructure announced by OpenAI or its competitors. (Opeli has not yet asked TechCrunch’s request for comment, but in order to be larger than Monaco in retrospect.)
The ZAA project, developed in cooperation with the G42-Konglomerate with headquarters in Abu Zabi- is an element of the ambitious Stargate OpenAI project, Joint Venture announced in January, where in January could see mass data centers around the globe supplied with the event of AI.
While the primary Stargate campus in the United States – already in Abilene in Texas – is to realize 1.2 gigawatts, this counterpart from the Middle East will be more than 4 times.
The project appears among the many wider AI between the USA and Zea, which were a few years old, and annoyed some legislators.
OpenAI reports from ZAA come from 2023 Partnership With G42, the pursuit of AI adoption in the Middle East. During the conversation earlier in Abu Dhabi, the final director of Opeli, Altman himself, praised Zea, saying: “He spoke about artificial intelligence Because it was cool before. “
As in the case of a big a part of the AI world, these relationships are … complicated. Established in 2018, G42 is chaired by Szejk Tahnoon Bin Zayed Al Nahyan, the national security advisor of ZAA and the younger brother of this country. His embrace by OpenAI raised concerns at the top of 2023 amongst American officials who were afraid that G42 could enable the Chinese government access advanced American technology.
These fears focused on “G42”Active relationships“With Blalisted entities, including Huawei and Beijing Genomics Institute, in addition to those related to people related to Chinese intelligence efforts.
After pressure from American legislators, CEO G42 told Bloomberg At the start of 2024, the corporate modified its strategy, saying: “All our Chinese investments that were previously collected. For this reason, of course, we no longer need any physical presence in China.”
Shortly afterwards, Microsoft – the fundamental shareholder of Opeli together with his own wider interests in the region – announced an investment of $ 1.5 billion in G42, and its president Brad Smith joined the board of G42.
(Tagstransate) Abu dhabi
-

 Press Release1 year ago
Press Release1 year agoU.S.-Africa Chamber of Commerce Appoints Robert Alexander of 360WiseMedia as Board Director
-

 Press Release1 year ago
Press Release1 year agoCEO of 360WiSE Launches Mentorship Program in Overtown Miami FL
-

 Business and Finance12 months ago
Business and Finance12 months agoThe Importance of Owning Your Distribution Media Platform
-

 Business and Finance1 year ago
Business and Finance1 year ago360Wise Media and McDonald’s NY Tri-State Owner Operators Celebrate Success of “Faces of Black History” Campaign with Over 2 Million Event Visits
-

 Ben Crump1 year ago
Ben Crump1 year agoAnother lawsuit accuses Google of bias against Black minority employees
-

 Theater1 year ago
Theater1 year agoTelling the story of the Apollo Theater
-

 Ben Crump1 year ago
Ben Crump1 year agoHenrietta Lacks’ family members reach an agreement after her cells undergo advanced medical tests
-

 Ben Crump1 year ago
Ben Crump1 year agoThe families of George Floyd and Daunte Wright hold an emotional press conference in Minneapolis
-

 Theater1 year ago
Theater1 year agoApplications open for the 2020-2021 Soul Producing National Black Theater residency – Black Theater Matters
-

 Theater12 months ago
Theater12 months agoCultural icon Apollo Theater sets new goals on the occasion of its 85th anniversary











