For many individuals in Great Britain, it changes: how we work, what we do and where we do it. Change is quicker for some than for others – and does not at all times change for the higher.
New national study – organized and managed by my colleagues and I – paints a mixed picture of professional life in Great Britain. What makes him Testing skills and employment 2024 It is exclusive that it’s eighth in a series that dates back to the mid -Eighties.
The survey focuses on the professional life of individuals: what skills they use and where they work and what they consider their work. The data series consists of interviews of just about 35,000 employees, with about 5500 in 2024.
Some people have good things to say about changing professional life. Other people’s professional life is just not improving. For a lot of us it’s a little bit of each.
Good news
One of the excellent news is that only a few employees think that their work has no value. Against estimates Through some scholars that about 40% of individuals “work on tasks they consider to be pointless”, our study suggests that only 5% of respondents imagine that their work is irrelevant and has no value.
So -called “Bullshit Jobs” They are rare. Instead, almost 70% reported that their work gave them a way of feat at all times or more often than not, while 76% stated that their work was useful.
Work becomes more qualified too. In 2024, 46% of employees stated that they would want qualifications on the graduate level in the event that they were to use for his or her current job. It increases from 20% in 1986.
Another excellent news is that the pace of excessive qualification has dropped. In 2024, 35% of employees reported that they’d qualifications that were higher than those currently required to work in comparison with 39% in 2006.
. Quality of labor sex gap It is narrowing. The difference in salaries was consistently falling, however the gap in the physical work environment – in the standard of labor and professional skills – also narrow. For example, the share of men who reported that their health or security was threatened due to work from 38% in 2001 to 21% in 2024, while amongst women remained stable at 22%.
Bad news
However, not every thing in the world of labor. Abuse of workplace It is common – 14% of British employees have experienced intimidation, violence or sexual harassment at work. The risk of abuse is far higher in women, LGBTQ+employees, nurses, teachers and those that work at night.
Alan Felstead/Skills and Employment Survey 2024IN Author given (without reuse)
One of probably the most striking findings from our study is a big decrease in ability Employees to make decisions About their immediate professional tasks. In 2024, 34% of employees stated that they’d a “great influence” on what tasks they performed, how they did them and the way they worked hard. In 2012, it’s a decrease in 44% in 1992.
The mechanisms of greater worker control increased over time, but this didn’t translate into greater control at the person level.
Mixed news
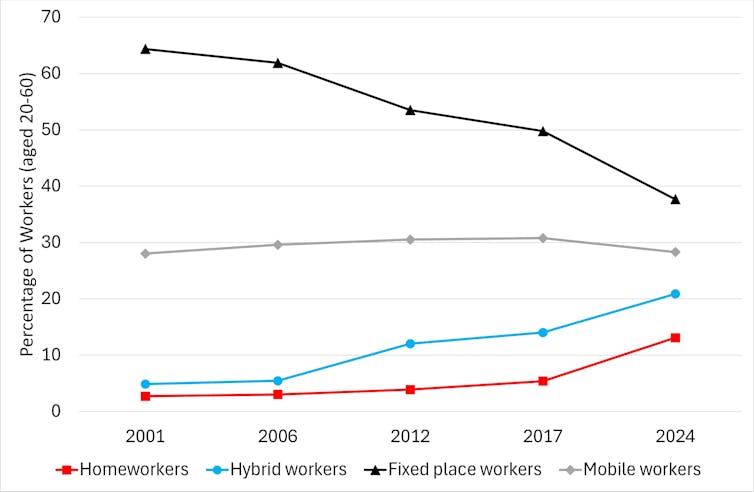
Another striking, if not surprising, the statement is to extend the number of individuals Woking from home. But the long nature of change could also be a surprise. The study shows that the rise in hybrid work began in 2006, long before this date.
The survey also sheds light on where they work from home. It shows that 45% may isolate themselves from others in the household, making a home office. The rest have to be content with a kitchen table, sofa or corner of the room.
Alan Felstead/Skills and Employment Survey 2024IN Author given (without reuse)
After years of falling membership in the Trade Union, the study shows that the wave may ultimately They turned around. Levels of membership increased, and the rates of trade union presence in the workplace and the impact of unions on remuneration increased in 2017-2024.
The growing a part of the members of trade unions claims that their relationship has a big or significant impact on the best way of organizing work – in comparison with 42% in 2001 to 51% in 2024.
The technological change brings each possibilities and advantages. This study showed Digital technology He played a job in just about all workplaces, and 78% of employees are considering “necessary” or “very important” computers in their work, in comparison with 45% in 1997.
The participation of AI users increased throughout the data collection period, which indicates its quick acceptance. But there are few signs that they’re displacing employees, a minimum of for now.
Regular monitoring of all problems raised here – and lots of besides – is just possible if regular and solid research, reminiscent of Skills and employment test are carried out. These are invaluable elements of our knowledge infrastructure that have to be valued, protected and supported if we’re to evaluate exactly how the world of labor changes.